Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Does Progress
Cerebral small vessel disease does progress. Cerebral small vessel diseases SVD have been causally correlated with ischemic strokes leading to cognitive decline and vascular dementia. Because most brain tissue appears white on MRIs these abnormalities were historically referred to as white matter changes. Footnotes Correspondence to Monique M.
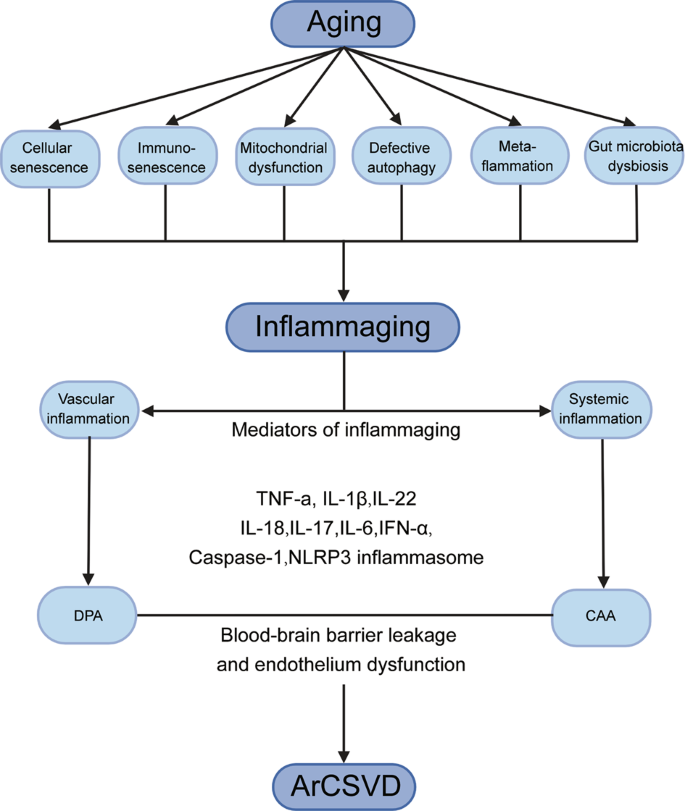
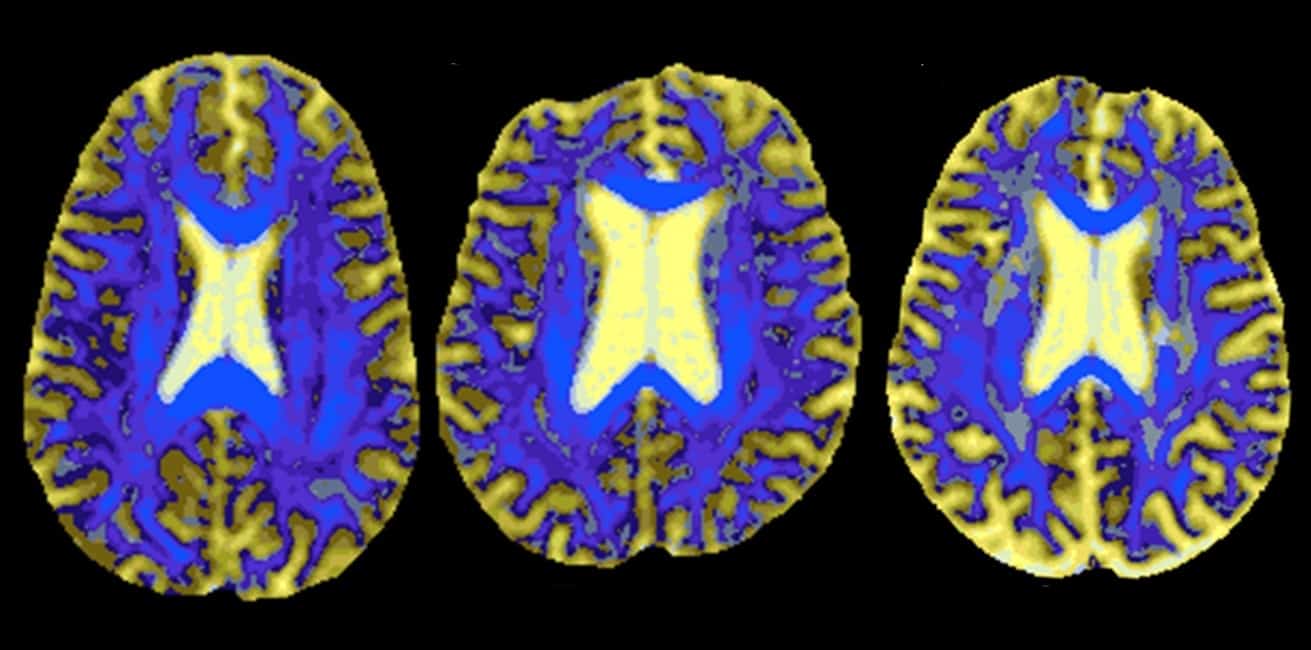
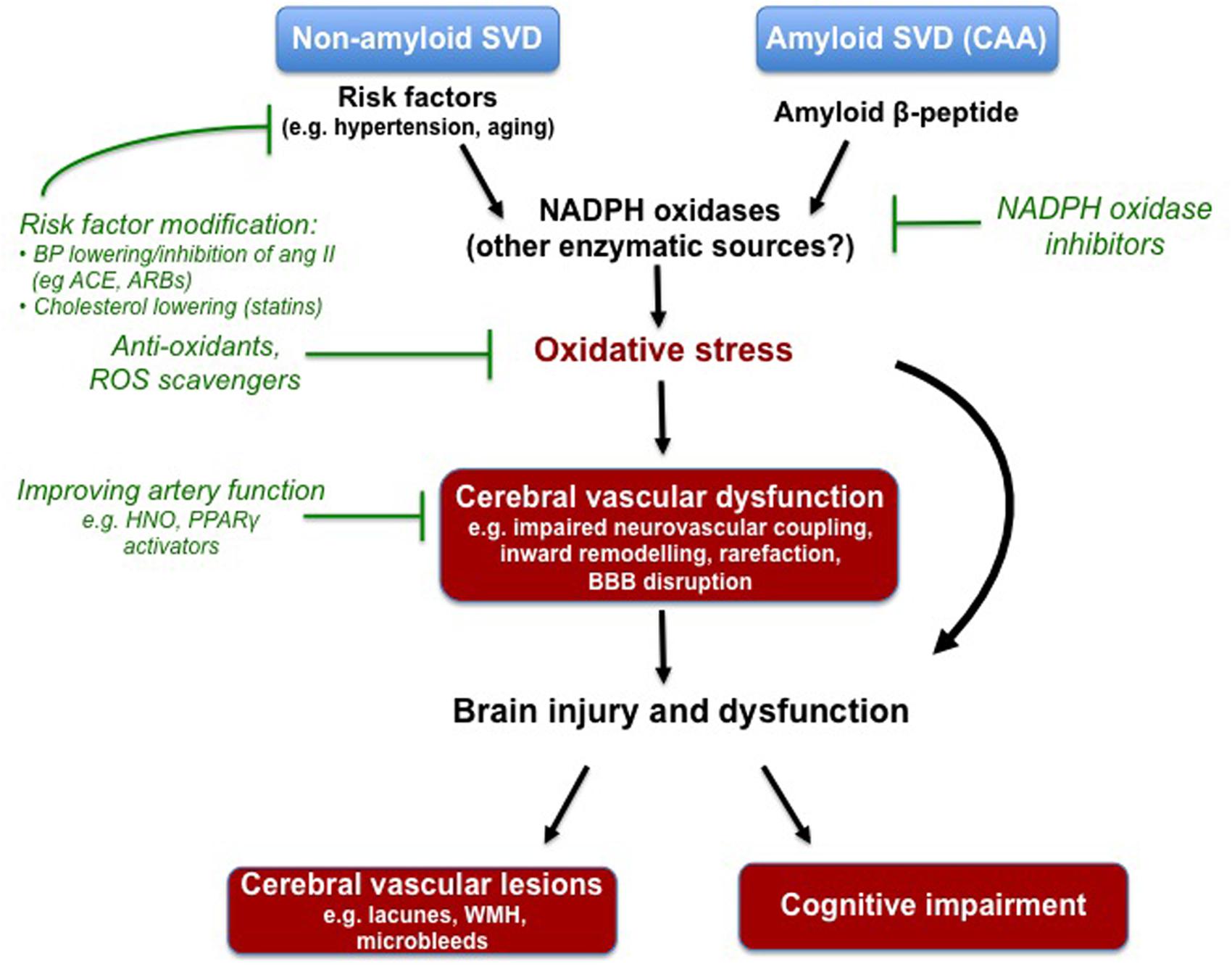
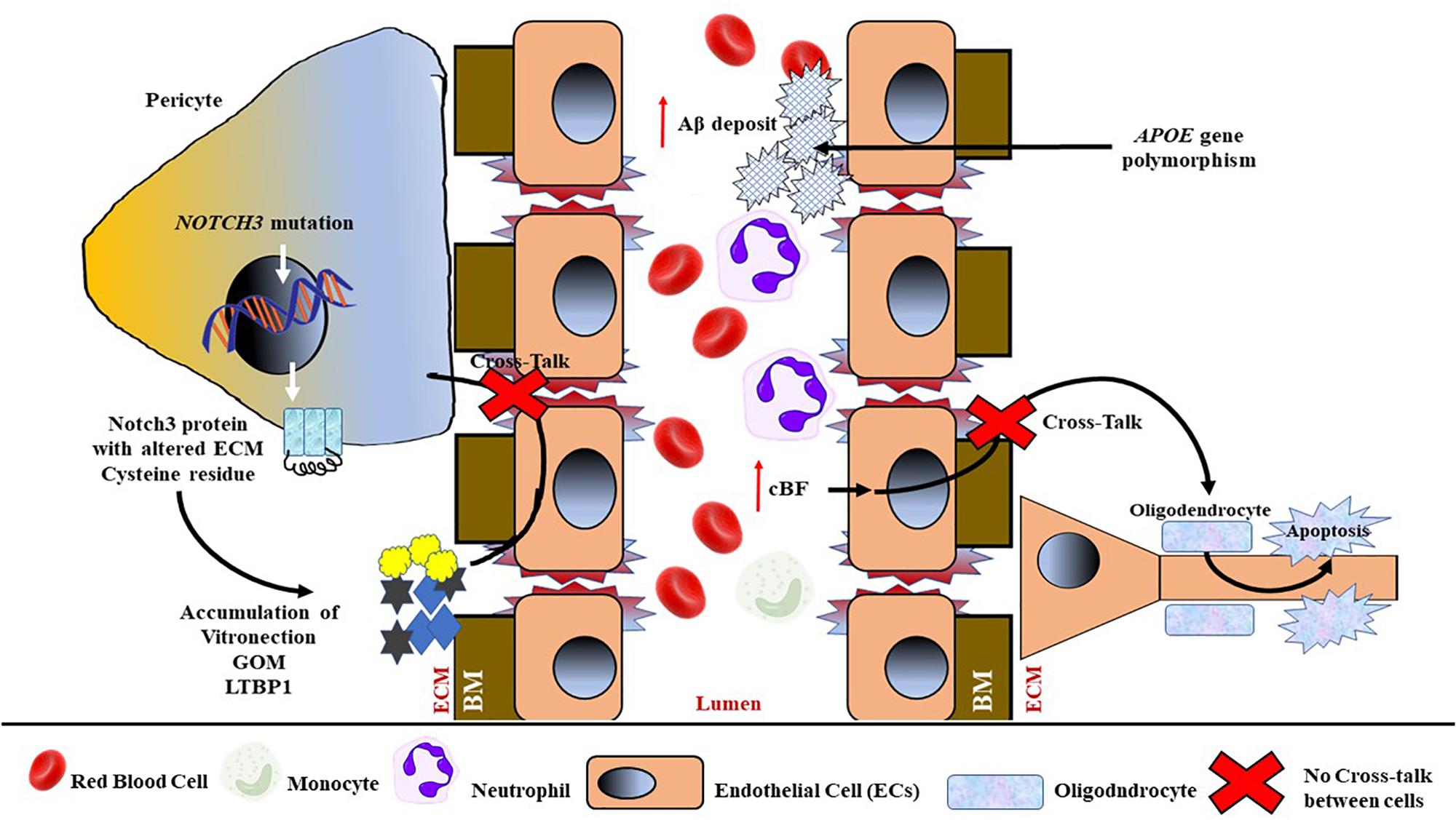
SVD has an inherent tendency to progress but data on its natural course are sparse and there are almost no drug trials dedicated to it. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is characterized by changes in the pial and parenchymal microcirculations. But its effects can also be more subtle causing walking and.
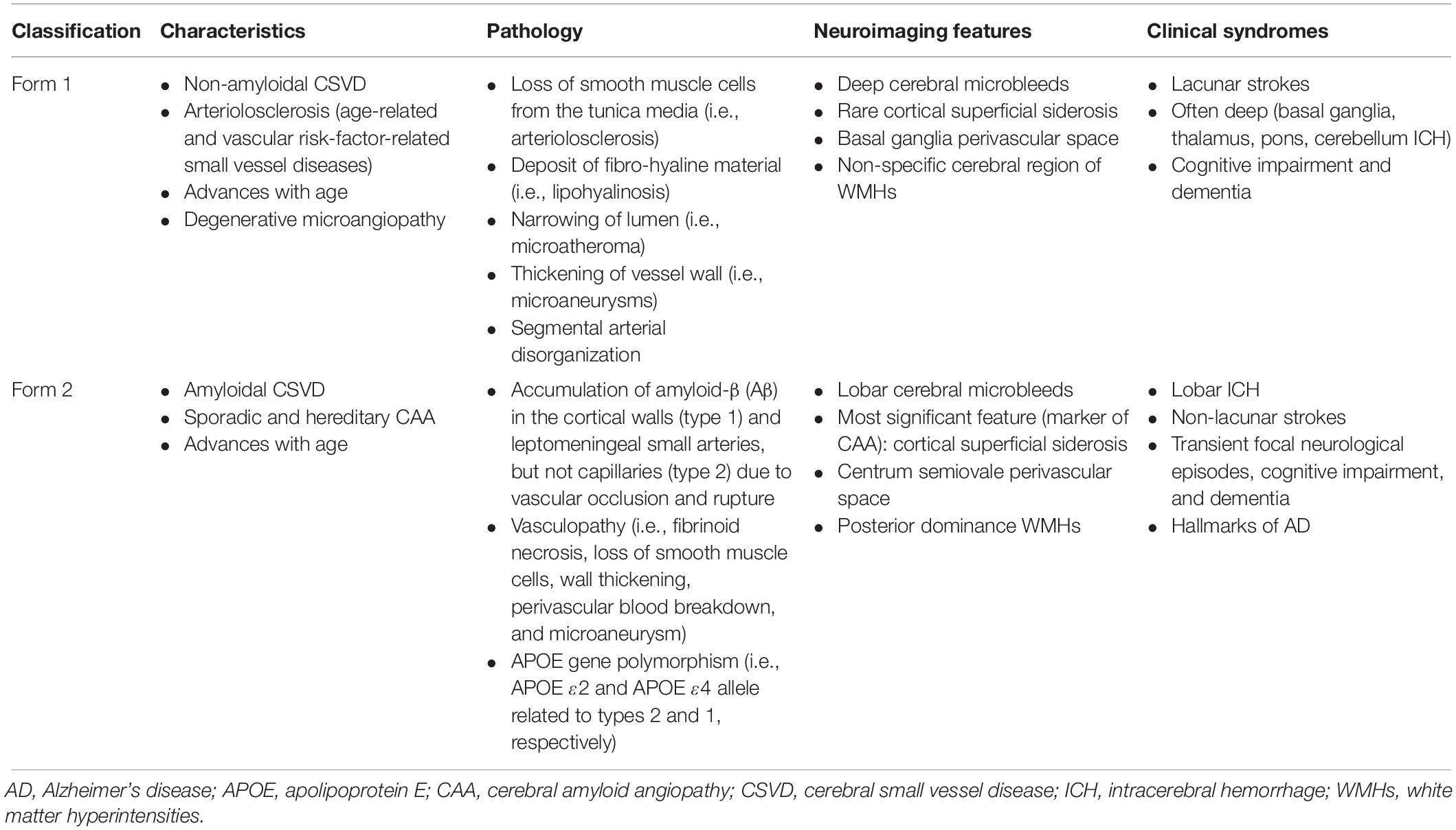
Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is an umbrella term covering a variety of abnormalities related to small blood vessels in the brain. It is the result of brain damage due to reduced or blocked blood flow in blood vessels in your brain. It reduces blood flow so the supply of energy and oxygen to the brain and the removal of waste become less efficient.
In some people the small vessels become damaged. This damage called cerebral small vessel disease increases the risk of stroke and cognitive decline including vascular dementia the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimers disease especially when its coupled with conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes. SVD is also frequent among clinically healthy subjects and patients with.
Neuroimaging and molecular genetic tests could improve diagnostic accuracy in patients with potential SVD. SVD-dementia is characterised by a dysexecutive type of cognitive impairment neurological deficits including imbalance and voiding dysfunction and emotional disturbances. This in turn leads to damage to the brain itself.
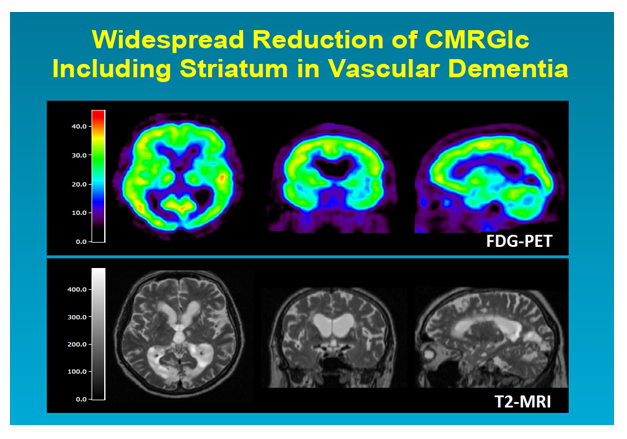
Small vessel disease SVD or microangiopathy of the cerebral white and central grey matter is an important subtype of vascular dementia VD. This is known as small vessel disease. Thats according to a s.
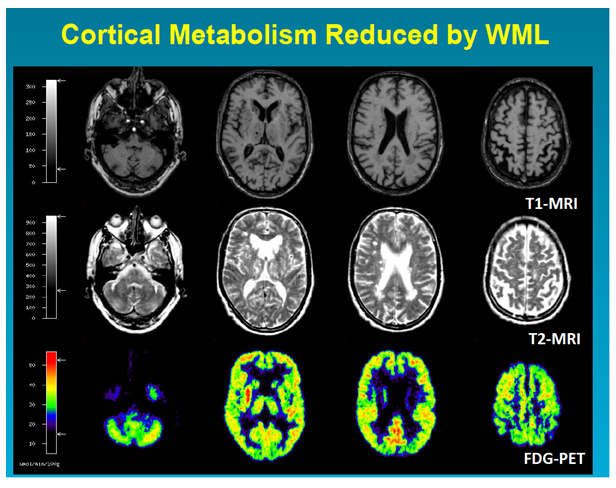
SVD produces reductions in cerebral blood flow and impaired blood-brain barrier function which are leading contributors to age-related reductions in brain health. This damage can be caused by stroke infection of a heart valve endocarditis or other blood vessel conditions that deprive brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients.
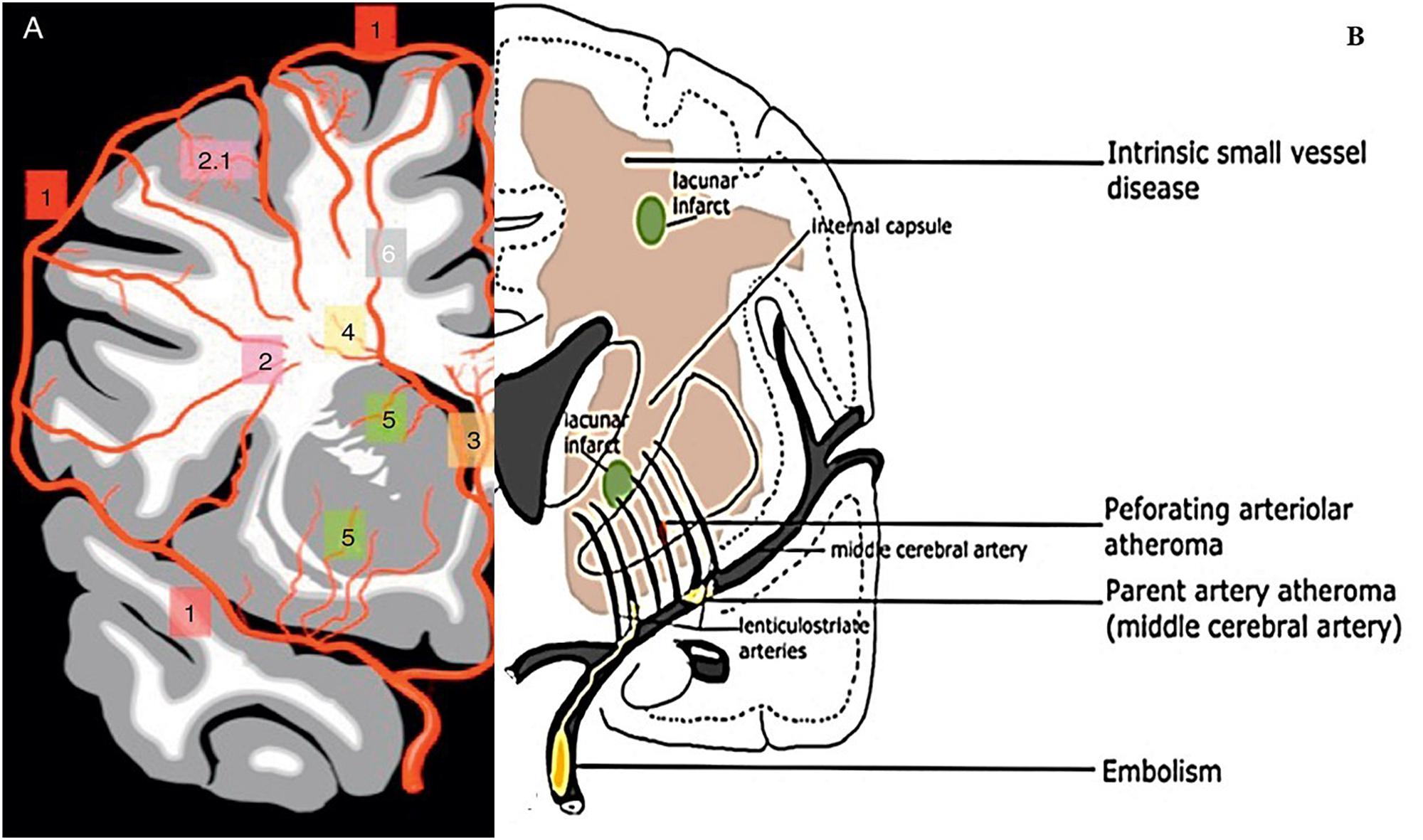
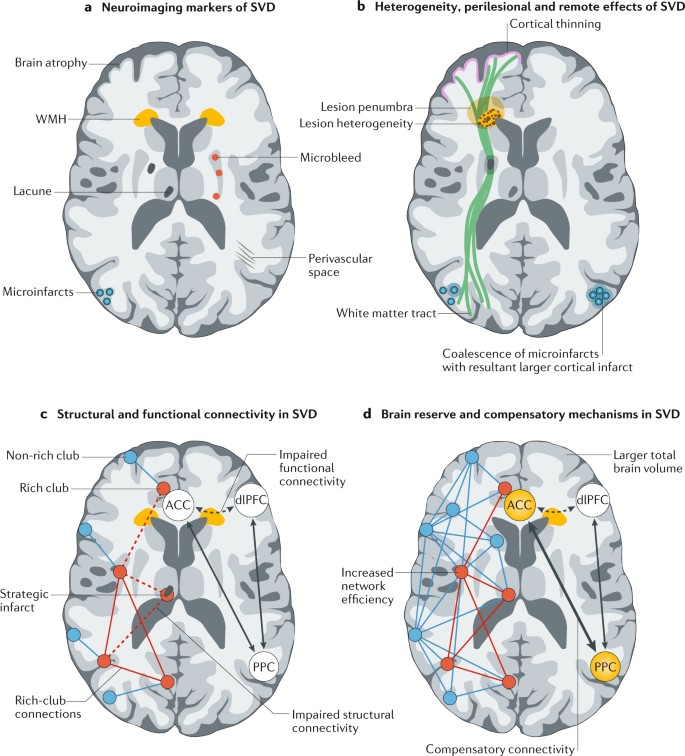
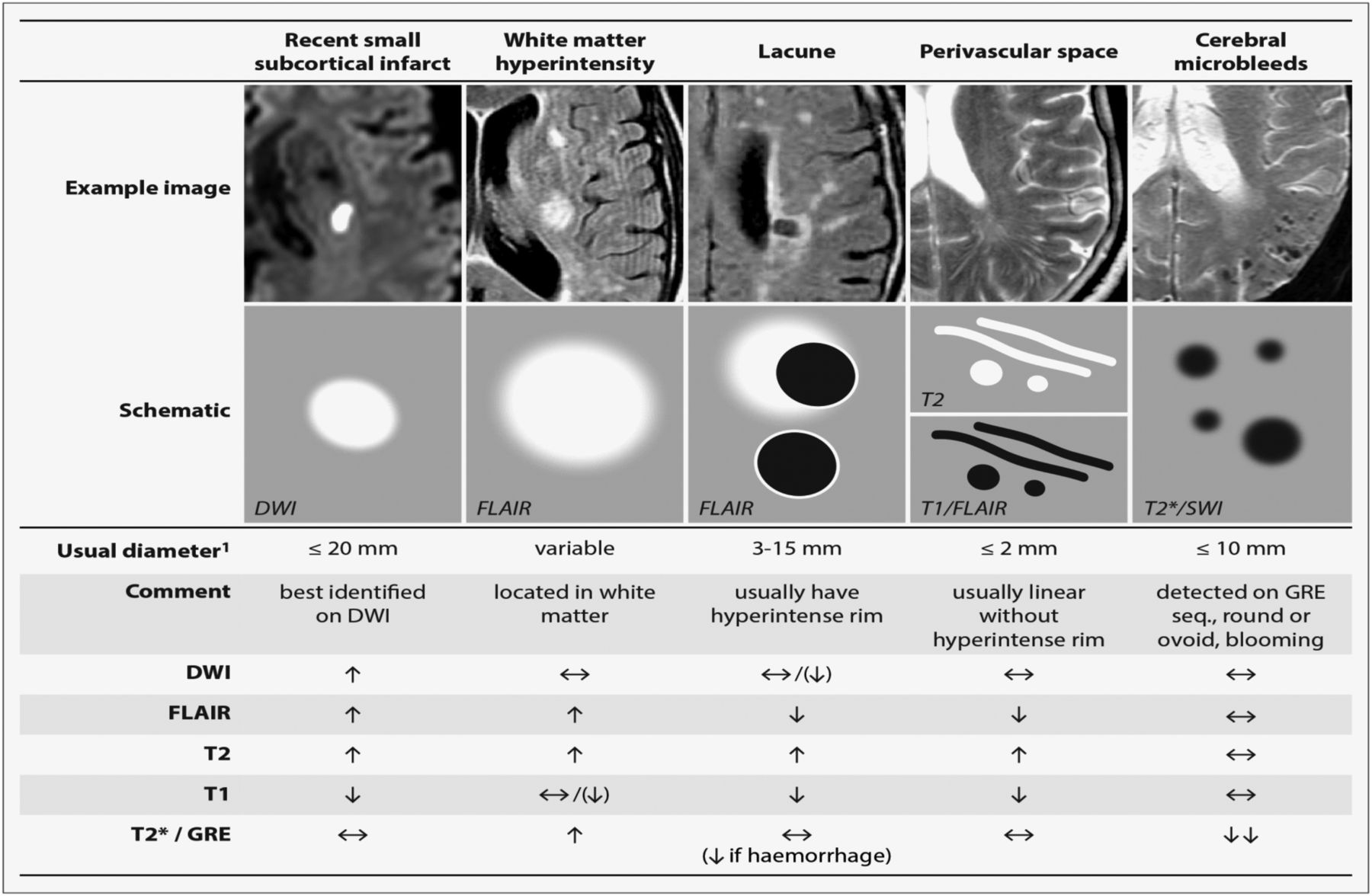
Cerebral small vessel disease SVD includes pathology of the brains small arteries arterioles capillaries venules and veins1 Key risk factors for SVD include age and cardiovascular risk factors23 although vascular risk does not fully account for SVD pointing to its multifactorial nature and as of yet unclear underlying mechanism.
I also have a bilateral nystagmus and an elevated CSF protein level. Basically is cerebral small vessel disease always progressive. This damage called cerebral small vessel disease increases the risk of stroke and cognitive decline including vascular dementia the second most common form of dementia after Alzheimers disease especially when its coupled with conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes. It is the result of brain damage due to reduced or blocked blood flow in blood vessels in your brain. Small vessel disease SVD or microangiopathy of the cerebral white and central grey matter is an important subtype of vascular dementia VD. Within minutes brain cells begin to. But its effects can also be more subtle causing walking and. This article reviews the evidence on the speed and predictors of progression of SVD in regard to cognitive deficits functional decline and white matter lesions as derived from epidemiological clinical and imaging studies and the placebo branches of VD drug trials. In some people the small vessels become damaged.
Breteler MD PhD Department of Epidemiology Biostatistics Erasmus Medical Center PO Box 1738 3000DR Rotterdam The Netherlands. This article reviews the evidence on the speed and predictors of progression of SVD in regard to cognitive deficits functional decline and white matter lesions as derived from epidemiological clinical and imaging studies and the placebo branches of VD drug trials. Cerebral small vessel diseases SVD have been causally correlated with ischemic strokes leading to cognitive decline and vascular dementia. Within minutes brain cells begin to. SVD-dementia is characterised by a dysexecutive type of cognitive impairment neurological deficits including imbalance and voiding dysfunction and emotional disturbances. In some people the small vessels become damaged. Total homocysteine tHCY might increase the risk of myocardial and cerebral infarction by damaging vascular endothelium.





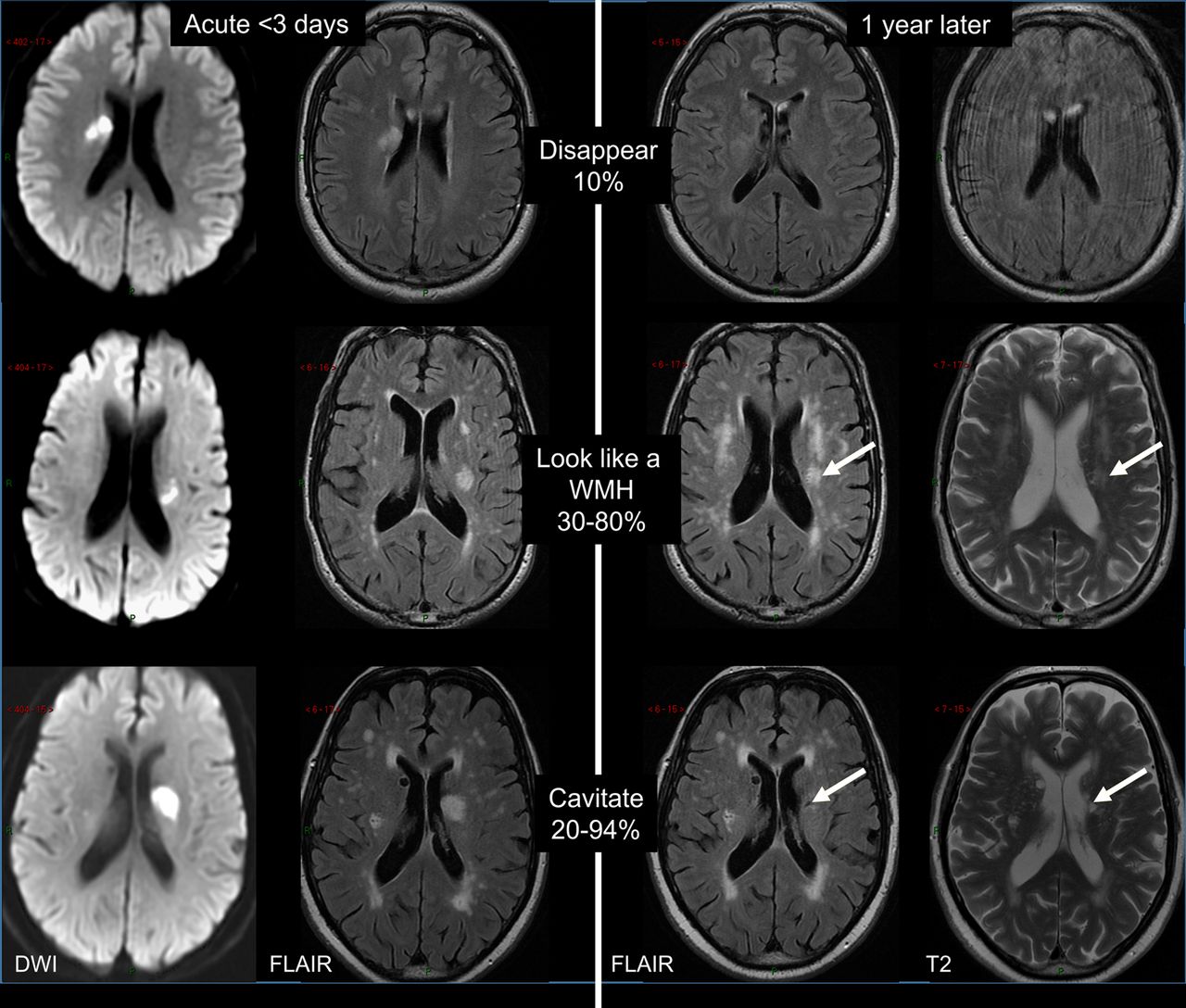


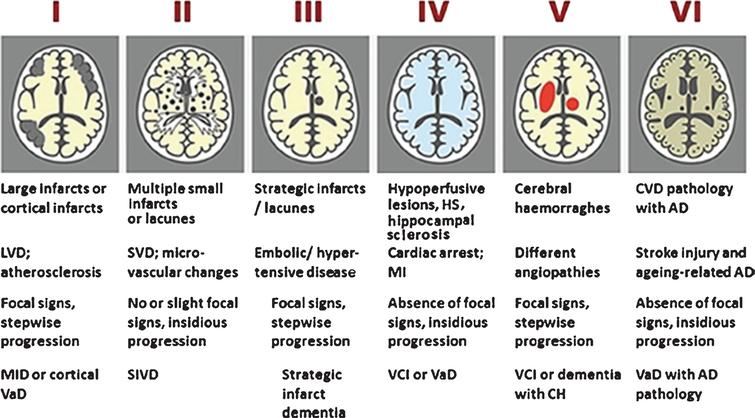
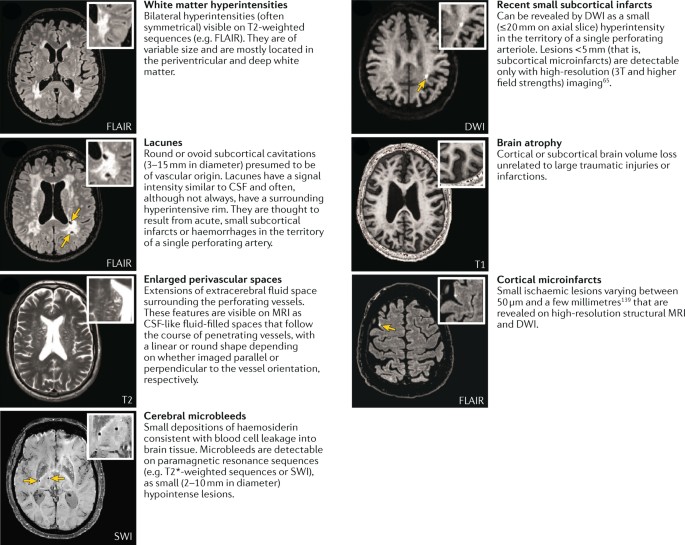

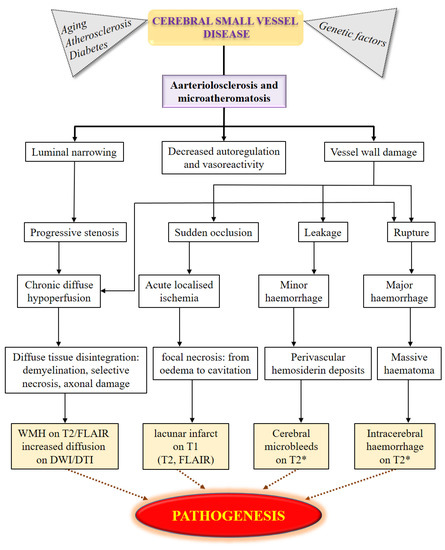





















Post a Comment for "Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Does Progress"